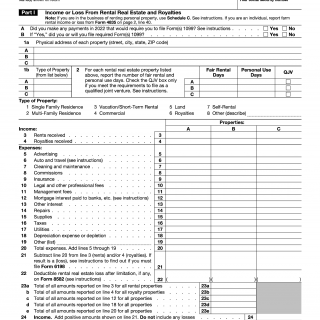
IRS Form 1040 Schedule E. Supplemental Income and Loss
IRS Form 1040 Schedule E consists of several parts that details the supplemental income and losses for a taxpayer. It is typically used by taxpayers who have income from rental property, a business, royalty income, estate/trust distributions, or a partnership. The form is used to report the income or loss from these activities and it can be issued by individuals or corporations. The form requires the taxpayer to provide details on their income sources, expenses, and any applicable deductions. It is important to note that any losses reported here cannot be used to reduce your income on your tax return, they can only be used to create a net loss that can be applied against future income.
When filling out the form, information regarding the activity being reported should be included such as the name of the business, the type of business, the income and expense statements, depreciation schedules, and any sales or mortgage information. Supporting documents, such as leases, bank statements, and other proof of income and expense, should be kept and attached. Additionally, when reporting rental property, information regarding the property location, acquisition date, sale date, and Net Investment Income Tax (NIIT) should be provided as well.
One strength of Form 1040 Schedule E is that it allows taxpayers to accurately report their supplemental income and any losses associated with those activities. It contains important fields to help ensure the information is collected in a standard format. Additionally, it allows taxpayers to report income and losses separately; this allows them to take advantage of deductions and efficiently report taxes due.
A potential weakness of the form could be confusion on the part of the taxpayers, especially when it comes to understanding the details and being able to accurately report the different types of incomes and expenses associated with them. Additionally, the form is subject to change depending on the current tax laws. Therefore, depending on the tax year, changes might be made to the form which could potentially result in confusion for taxpayers.
In terms of opportunities, Form 1040 Schedule E allows taxpayers to accurately report the income and losses associated with their supplemental income activities and take any applicable deductions. Additionally, it provides taxpayers with the opportunity to save money on their taxes, and they may be eligible for tax deductions that they would otherwise not be able to take advantage of.
In terms of threats, taxpayers may face penalties if they have inaccurately filed their Form 1040 Schedule E or if they have failed to include any of the required documents. It is important to understand the form and to accurately report your income and expenses in order to avoid any potential penalties.
Form 1040 Schedule E is typically submitted with a tax return, or it can be filed separately. It is important to keep all of the documents associated the form in a safe place. They should be kept for at least three years after filing.
Form 1040 Schedule E is related to other forms, such as Form 1040 Schedule C (used to report income or losses from a business), Form 1040 Schedule K-1 (used to report income or losses from a partnership) and Form 1040 Schedule D (used to report capital gains and losses). The differences between these forms include the type of income or losses being reported and the deductions that can be taken.
In conclusion, Form 1040 Schedule E is an important form for taxpayers to understand and report their supplemental income and losses. It is important to accurately report the information and to keep any relevant documents associated with it. By understanding the form and reporting accurately, taxpayers can potentially save money on their taxes and avoid any penalties associated with filing inaccurately.